Solids, Liquids and Gases
We're back at Year 9
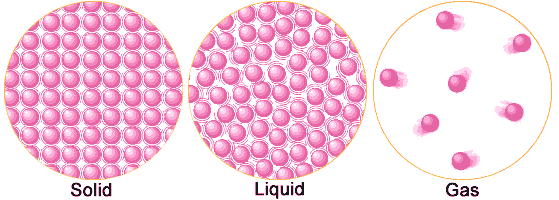
Solids, Liquids and Gases have macro and microscopic properties
Macroscopic Properties
Solid Particles are in very close proximity to each other
Solids, Liquids and Gases have macro and microscopic properties
Macroscopic Properties
Solid Particles are in very close proximity to each other
Brownian Motion
The random movement of microscopic particles suspended in a fluid (fluid doesn't necessarily mean liquid)
This is basically the movement of particles in matter
In Solids
Particles in a solid vibrate around a fixed point of equilibrium. They can't move about the structure
In Liquids
Particles in a liquid mostly vibrate but can move about the structure
In Gases
Particles in a gas don't change direction unless collide with another particle
This is basically the movement of particles in matter
In Solids
Particles in a solid vibrate around a fixed point of equilibrium. They can't move about the structure
In Liquids
Particles in a liquid mostly vibrate but can move about the structure
In Gases
Particles in a gas don't change direction unless collide with another particle
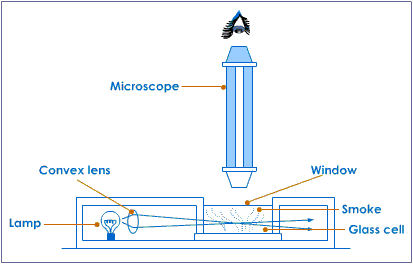
Observing Brownian Motion
Brownian Motion can be observed if you focus light onto smoke in a gas chamber below a microscope. The microscope needs to be focused onto the smoke particles. You will see small light spots through the microscope and over time these will slowly move in a random fashion due the collisions with the gas molecules.
Go to the link below to observe what is going on under the microscope.
Go to the link below to observe what is going on under the microscope.
http://www.kscience.co.uk/animations/brownian.swf
Internal Energy
In a real gas internal energy is the potential energy and kinetic energy
In an ideal gas however only the kinetic energy is taken into account because no energy is lost to potential energy during the collisions of the particles
In an ideal gas however only the kinetic energy is taken into account because no energy is lost to potential energy during the collisions of the particles