Arenes
Arenes are hydrocarbons based on benzene C6H6
The ring is there instead of three double bonds due to the dissociation of the electrons which 'sit' on top of the ring.
At each corner is one carbon and one hydrogen.
At each corner is one carbon and one hydrogen.
These compounds are named as either the benzene group or the phenyl group depending on the functional groups present.
This would be called 1-methylbenzene. It doesn't matter where carbon number 1 is if benzene is the only functional group present.
This is 1-bromo-3,4-dimethylbenzene
This is phenylamine
Stability of Benzene Ring
|
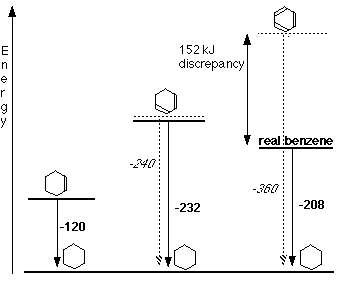
Originally the Benzene ring was modeled with the Kekulé Model. This worked on the basis that the pi bonds were secure in one exact position. However through viewing the enthalpies the Kekulé model stopped fitting. As the graph below shows the theoretical enthalpy change of benzene should be higher than it is in reality. This is because of the delocalised ring of electrons increasing the structures stability.
|
Electrophilic Substitution
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Benzene Rings undergo Friedel-Crafts Acylation through the mechanism electrophilic substitution.
The reaction is between benzene and an acyl chloride creating a phenylketone and hydrochloric acid
The catalyst is AlCl3
The reaction is between benzene and an acyl chloride creating a phenylketone and hydrochloric acid
The catalyst is AlCl3
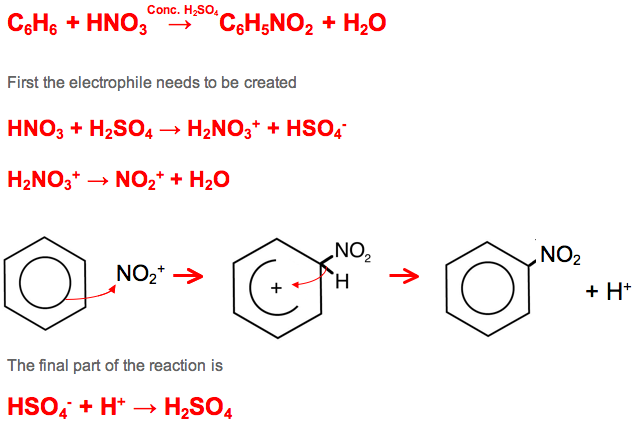
Remember electrophiles attract electron density so we need to positive charge
Nitration
Benzene Rings also undergo Nitration through Electrophilic Substitution in order to create dyes and explosives
This occurs between benzene and concentrated nitric acid creating nitrobenzenes
The catalyst is concentrated sulphuric acid
This occurs between benzene and concentrated nitric acid creating nitrobenzenes
The catalyst is concentrated sulphuric acid
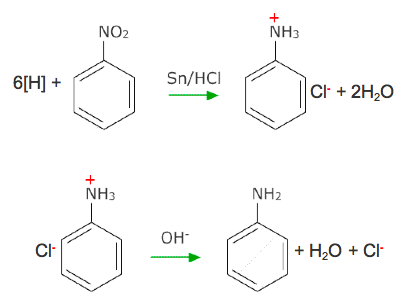
Reduction of Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is reduced to phenylamine and water.
The conditions necessary are Tin and concentrated HCl under reflux and sodium hydroxide solution.
The reduction occurs through two steps.
The first requires Tin and concentrated HCl under reflux. The result is a phenylammonium salt and water
The conditions necessary are Tin and concentrated HCl under reflux and sodium hydroxide solution.
The reduction occurs through two steps.
The first requires Tin and concentrated HCl under reflux. The result is a phenylammonium salt and water